Associação Portuguesa de Investigação em Cancro
O impacto da ativação do KRAS na modulação do microambiente tumoral
O impacto da ativação do KRAS na modulação do microambiente tumoral
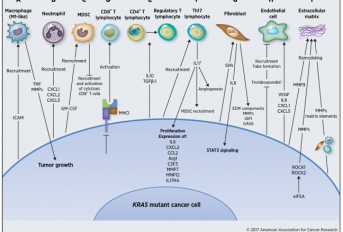
Este trabalho faz uma revisão da literatura dos aspetos relacionados com as alterações no microambiente tumoral induzidas pela ativação do KRAS nas células tumorais. Destacam-se novos mecanismos de progressão tumoral induzida pelo KRAS que podem ter um grande impacto no desenvolvimento de novas terapias que tenham como alvo a eliminação das células tumorais interferindo com as suas interações com o microambiente tumoral.
Autores e Afiliações:
Patrícia Dias Carvalho 1,2, Carlos F. Guimarães 1,2, Ana P. Cardoso 1,3, Susana Mendonca 1,2, Ângela M Costa 1,3, Maria J. Oliveira 1,3,4, and Sérgia Velho 1,2
1 i3S - Instituto de Investigação e Inovação em Saúde, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal.
2 IPATIMUP - Institute of Molecular Pathology and Immunology of the University of Porto, Porto, Portugal.
3 INEB – Institute of Biomedical Engineering, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal.
4 Faculty of Medicine of the University of Porto, Porto, Portugal.
Abstract:
KRAS is one of the most frequently mutated oncogenes in cancer, being a potent initiator of tumorigenesis, a strong inductor of malignancy, and a predictive biomarker of response to therapy. Despite the large investment to understand the effects of KRAS activation in cancer cells, pharmacologic targeting of KRAS or its downstream effectors has not yet been successful at the clinical level. Recent studies are now describing new mechanisms of KRAS-induced tumorigenesis by analyzing its effects on the components of the tumor microenvironment. These studies revealed that the activation of KRAS on cancer cells extends to the surrounding microenvironment, affecting the properties and functions of its constituents. Herein, we discuss the most emergent perspectives on the relationship between KRAS-mutant cancer cells and their microenvironment components.
Revista: Cancer Research




